UnsAIfe
AI systems are moving from novelty to infrastructure. They write, code, search, and increasingly act on our behalf.
That speed has put a spotlight on a harder question: how seriously are AI companies managing the risks that come with more capable models?
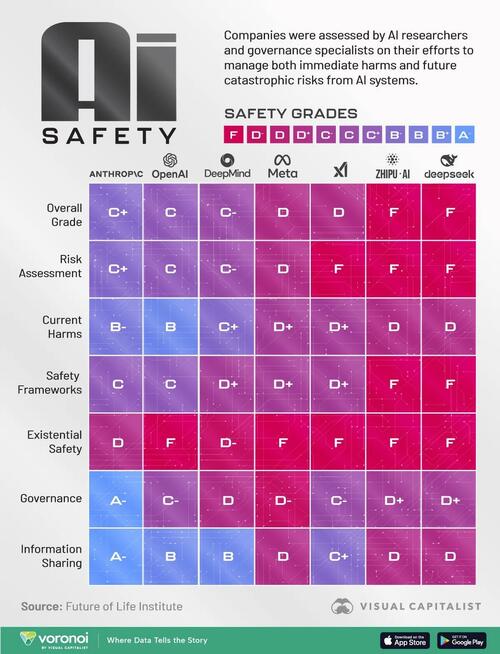
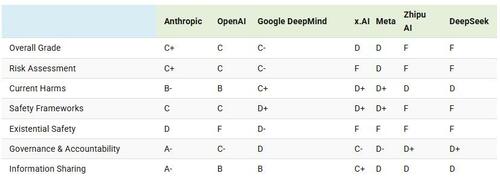
This graphic, via Visual Capitalist's Niccolo Conte, visualizes and compares the safety scores of major AI companies using data from the AI Safety Index published by the Future of Life Institute, which scores companies across six key metrics.
Which AI Companies Prioritize Safety Most?Based on the scores across six key metrics of AI safety, Anthropic, the creators of Claude, scored highest overall with a C+.
Anthropic was the only company that scored an “A” grade in two categories, with an A- in both governance and accountability along with information sharing.
The table below shows the overall grade of each AI company in terms of safety, along with their grades in specific safety categories.
Following Anthropic was OpenAI, creators of ChatGPT, which received a C grade overall. The only category it scored higher than Anthropic in was in the current harms category, partially thanks to the fact that OpenAI was the only company with a published whistleblowing policy at the time of the report’s publication.
Chinese companies Zhipu.AI and DeepSeek both received failing grades overall, though the report notes that China’s stricter national AI regulations may explain their weaker performance on Western-aligned self-governance and transparency metrics.
Understanding “AI Safety” and Why it MattersA useful AI safety program is more than a promise to “be responsible.” It shows up as concrete processes: documented evaluations, clear thresholds for when to pause or limit deployment, and a trail of public reporting that lets outsiders understand what was tested and why.
Companies that score well tend to communicate more about how they handle model behavior, misuse risks, and incident response.
In contrast, lower-rated firms often appear opaque—either disclosing less overall or providing safety statements that are hard to verify.
In highlighting companies’ weak points when it comes to AI safety, the report from the Future of Life Institute notes that the AI industry is both fundamentally unprepared for its stated goals of reaching artificial general intelligence (AGI).
Along with this, it states that AI capabilities are accelerating far faster than risk management practices, and the lack of a regulatory floor means companies can cut corners on safety in order to get ahead in the race towards AGI.
To learn more about AI companies, check out this graphic on Voronoi that charts the skyrocketing revenues of Anthropic, OpenAI, and xAI.
Loading recommendations...